- Class A Ip Address List
- Classes Of Ip Address
- Which Class Of Ip Address Your System Have Failed
- Ip Address Types Class
See full list on meridianoutpost.com. An Internet Protocol address (IP address) is a numerical label assigned to each device connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. An IP address serves two main functions: host or network interface identification and location addressing. Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) defines an IP address as a 32-bit number.
This article is intended as a general introduction to the concepts of Internet Protocol (IP) networks and subnetting. A glossary is included at the end of article.
Original product version: Windows 10 - all editions
Original KB number: 164015
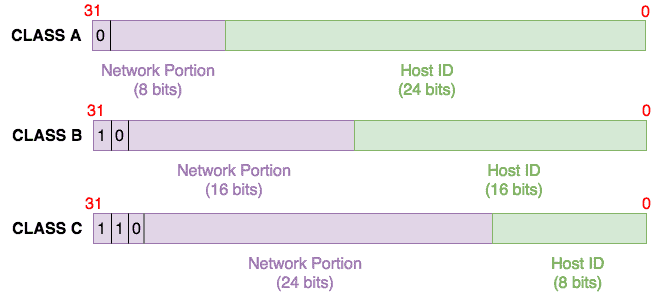
IP Address Class A, B and C Network and Host Capacities. In the preceding topics I introduced the concepts of IP address classes and showed how the classes related to ranges of IP addresses.Of the five classes, D and E are dedicated to special purposes, so I will leave those alone for now. Class C IP address always has its first bits as 110, next 21 bits as a network address and following 8 bits as the host address. The range of IP addresses is the first block from 192.0.0.0 to 192.0.0.255 and the last block from 223.255.255.0 to 223.255.255.255. This means that it allows 2^21 networks and 2^8 hosts per network.
Summary
When you configure the TCP/IP protocol on a Windows computer, the TCP/IP configuration settings require:
- An IP address
- A subnet mask
- A default gateway
To configure TCP/IP correctly, it's necessary to understand how TCP/IP networks are addressed and divided into networks and subnetworks.
The success of TCP/IP as the network protocol of the Internet is largely because of its ability to connect together networks of different sizes and systems of different types. These networks are arbitrarily defined into three main classes (along with a few others) that have predefined sizes. Each of them can be divided into smaller subnetworks by system administrators. A subnet mask is used to divide an IP address into two parts. One part identifies the host (computer), the other part identifies the network to which it belongs. To better understand how IP addresses and subnet masks work, look at an IP address and see how it's organized.
IP addresses: Networks and hosts
An IP address is a 32-bit number. It uniquely identifies a host (computer or other device, such as a printer or router) on a TCP/IP network.
IP addresses are normally expressed in dotted-decimal format, with four numbers separated by periods, such as 192.168.123.132. To understand how subnet masks are used to distinguish between hosts, networks, and subnetworks, examine an IP address in binary notation.
For example, the dotted-decimal IP address 192.168.123.132 is (in binary notation) the 32-bit number 110000000101000111101110000100. This number may be hard to make sense of, so divide it into four parts of eight binary digits.
These 8-bit sections are known as octets. The example IP address, then, becomes 11000000.10101000.01111011.10000100. This number only makes a little more sense, so for most uses, convert the binary address into dotted-decimal format (192.168.123.132). The decimal numbers separated by periods are the octets converted from binary to decimal notation.
For a TCP/IP wide area network (WAN) to work efficiently as a collection of networks, the routers that pass packets of data between networks don't know the exact location of a host for which a packet of information is destined. Routers only know what network the host is a member of and use information stored in their route table to determine how to get the packet to the destination host's network. After the packet is delivered to the destination's network, the packet is delivered to the appropriate host.
For this process to work, an IP address has two parts. The first part of an IP address is used as a network address, the last part as a host address. If you take the example 192.168.123.132 and divide it into these two parts, you get 192.168.123. Network .132 Host or 192.168.123.0 - network address. 0.0.0.132 - host address.
Subnet mask
The second item, which is required for TCP/IP to work, is the subnet mask. The subnet mask is used by the TCP/IP protocol to determine whether a host is on the local subnet or on a remote network.
In TCP/IP, the parts of the IP address that are used as the network and host addresses aren't fixed. Unless you have more information, the network and host addresses above can't be determined. This information is supplied in another 32-bit number called a subnet mask. The subnet mask is 255.255.255.0 in this example. It isn't obvious what this number means unless you know 255 in binary notation equals 11111111. So, the subnet mask is 11111111.11111111.11111111.0000000.
Lining up the IP address and the subnet mask together, the network, and host portions of the address can be separated:
11000000.10101000.01111011.10000100 - IP address (192.168.123.132)
11111111.11111111.11111111.00000000 - Subnet mask (255.255.255.0)
The first 24 bits (the number of ones in the subnet mask) are identified as the network address. The last 8 bits (the number of remaining zeros in the subnet mask) are identified as the host address. It gives you the following addresses:
11000000.10101000.01111011.00000000 - Network address (192.168.123.0)
00000000.00000000.00000000.10000100 - Host address (000.000.000.132)
So now you know, for this example using a 255.255.255.0 subnet mask, that the network ID is 192.168.123.0, and the host address is 0.0.0.132. When a packet arrives on the 192.168.123.0 subnet (from the local subnet or a remote network), and it has a destination address of 192.168.123.132, your computer will receive it from the network and process it.
Almost all decimal subnet masks convert to binary numbers that are all ones on the left and all zeros on the right. Some other common subnet masks are:
Decimal Binary 255.255.255.192 1111111.11111111.1111111.11000000 255.255.255.224 1111111.11111111.1111111.11100000
Internet RFC 1878 (available from InterNIC-Public Information Regarding Internet Domain Name Registration Services) describes the valid subnets and subnet masks that can be used on TCP/IP networks.
Network classes
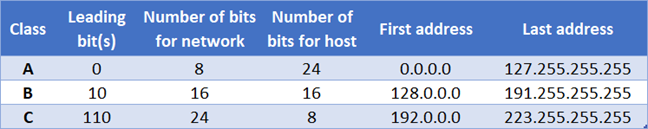
Internet addresses are allocated by the InterNIC, the organization that administers the Internet. These IP addresses are divided into classes. The most common of them are classes A, B, and C. Classes D and E exist, but aren't used by end users. Each of the address classes has a different default subnet mask. You can identify the class of an IP address by looking at its first octet. Following are the ranges of Class A, B, and C Internet addresses, each with an example address:
Class A networks use a default subnet mask of 255.0.0.0 and have 0-127 as their first octet. The address 10.52.36.11 is a class A address. Its first octet is 10, which is between 1 and 126, inclusive.
Class B networks use a default subnet mask of 255.255.0.0 and have 128-191 as their first octet. The address 172.16.52.63 is a class B address. Its first octet is 172, which is between 128 and 191, inclusive.
Class C networks use a default subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 and have 192-223 as their first octet. The address 192.168.123.132 is a class C address. Its first octet is 192, which is between 192 and 223, inclusive.
In some scenarios, the default subnet mask values don't fit the organization needs for one of the following reasons:
- The physical topology of the network
- The numbers of networks (or hosts) don't fit within the default subnet mask restrictions.
The next section explains how networks can be divided using subnet masks.
Subnetting
A Class A, B, or C TCP/IP network can be further divided, or subnetted, by a system administrator. It becomes necessary as you reconcile the logical address scheme of the Internet (the abstract world of IP addresses and subnets) with the physical networks in use by the real world.
A system administrator who is allocated a block of IP addresses may be administering networks that aren't organized in a way that easily fits these addresses. For example, you have a wide area network with 150 hosts on three networks (in different cities) that are connected by a TCP/IP router. Each of these three networks has 50 hosts. You are allocated the class C network 192.168.123.0. (For illustration, this address is actually from a range that isn't allocated on the Internet.) It means that you can use the addresses 192.168.123.1 to 192.168.123.254 for your 150 hosts.
Class A Ip Address List
Two addresses that can't be used in your example are 192.168.123.0 and 192.168.123.255 because binary addresses with a host portion of all ones and all zeros are invalid. The zero address is invalid because it's used to specify a network without specifying a host. The 255 address (in binary notation, a host address of all ones) is used to broadcast a message to every host on a network. Just remember that the first and last address in any network or subnet can't be assigned to any individual host.

You should now be able to give IP addresses to 254 hosts. It works fine if all 150 computers are on a single network. However, your 150 computers are on three separate physical networks. Instead of requesting more address blocks for each network, you divide your network into subnets that enable you to use one block of addresses on multiple physical networks.
In this case, you divide your network into four subnets by using a subnet mask that makes the network address larger and the possible range of host addresses smaller. In other words, you are 'borrowing' some of the bits used for the host address, and using them for the network portion of the address. The subnet mask 255.255.255.192 gives you four networks of 62 hosts each. It works because in binary notation, 255.255.255.192 is the same as 1111111.11111111.1111111.11000000. The first two digits of the last octet become network addresses, so you get the additional networks 00000000 (0), 01000000 (64), 10000000 (128) and 11000000 (192). (Some administrators will only use two of the subnetworks using 255.255.255.192 as a subnet mask. For more information on this topic, see RFC 1878.) In these four networks, the last six binary digits can be used for host addresses.
Using a subnet mask of 255.255.255.192, your 192.168.123.0 network then becomes the four networks 192.168.123.0, 192.168.123.64, 192.168.123.128 and 192.168.123.192. These four networks would have as valid host addresses:
192.168.123.1-62 192.168.123.65-126 192.168.123.129-190 192.168.123.193-254
Remember, again, that binary host addresses with all ones or all zeros are invalid, so you can't use addresses with the last octet of 0, 63, 64, 127, 128, 191, 192, or 255.
You can see how it works by looking at two host addresses, 192.168.123.71 and 192.168.123.133. If you used the default Class C subnet mask of 255.255.255.0, both addresses are on the 192.168.123.0 network. However, if you use the subnet mask of 255.255.255.192, they are on different networks; 192.168.123.71 is on the 192.168.123.64 network, 192.168.123.133 is on the 192.168.123.128 network.
Default gateways
If a TCP/IP computer needs to communicate with a host on another network, it will usually communicate through a device called a router. In TCP/IP terms, a router that is specified on a host, which links the host's subnet to other networks, is called a default gateway. This section explains how TCP/IP determines whether or not to send packets to its default gateway to reach another computer or device on the network.
When a host attempts to communicate with another device using TCP/IP, it performs a comparison process using the defined subnet mask and the destination IP address versus the subnet mask and its own IP address. The result of this comparison tells the computer whether the destination is a local host or a remote host.
If the result of this process determines the destination to be a local host, then the computer will send the packet on the local subnet. If the result of the comparison determines the destination to be a remote host, then the computer will forward the packet to the default gateway defined in its TCP/IP properties. It's then the responsibility of the router to forward the packet to the correct subnet.
Troubleshooting
TCP/IP network problems are often caused by incorrect configuration of the three main entries in a computer's TCP/IP properties. By understanding how errors in TCP/IP configuration affect network operations, you can solve many common TCP/IP problems.
Incorrect Subnet Mask: If a network uses a subnet mask other than the default mask for its address class, and a client is still configured with the default subnet mask for the address class, communication will fail to some nearby networks but not to distant ones. As an example, if you create four subnets (such as in the subnetting example) but use the incorrect subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 in your TCP/IP configuration, hosts won't be able to determine that some computers are on different subnets than their own. In this situation, packets destined for hosts on different physical networks that are part of the same Class C address won't be sent to a default gateway for delivery. A common symptom of this issue is when a computer can communicate with hosts that are on its local network and can talk to all remote networks except those networks that are nearby and have the same class A, B, or C address. To fix this problem, just enter the correct subnet mask in the TCP/IP configuration for that host.
Incorrect IP Address: If you put computers with IP addresses that should be on separate subnets on a local network with each other, they won't be able to communicate. They'll try to send packets to each other through a router that can't forward them correctly. A symptom of this problem is a computer that can talk to hosts on remote networks, but can't communicate with some or all computers on their local network. To correct this problem, make sure all computers on the same physical network have IP addresses on the same IP subnet. If you run out of IP addresses on a single network segment, there are solutions that go beyond the scope of this article.
Incorrect Default Gateway: A computer configured with an incorrect default gateway can communicate with hosts on its own network segment. But it will fail to communicate with hosts on some or all remote networks. A host can communicate with some remote networks but not others if the following conditions are true:
- A single physical network has more than one router.
- The wrong router is configured as a default gateway.
This problem is common if an organization has a router to an internal TCP/IP network and another router connected to the Internet.
References
Two popular references on TCP/IP are:
- 'TCP/IP Illustrated, Volume 1: The Protocols,' Richard Stevens, Addison Wesley, 1994
- 'Internetworking with TCP/IP, Volume 1: Principles, Protocols, and Architecture,' Douglas E. Comer, Prentice Hall, 1995
It is recommended that a system administrator responsible for TCP/IP networks have at least one of these references available.
Glossary
Broadcast address--An IP address with a host portion that is all ones.
Host--A computer or other device on a TCP/IP network.
Internet--The global collection of networks that are connected together and share a common range of IP addresses.
InterNIC--The organization responsible for administration of IP addresses on the Internet.
IP--The network protocol used for sending network packets over a TCP/IP network or the Internet.
IP Address--A unique 32-bit address for a host on a TCP/IP network or internetwork.
Network--There are two uses of the term network in this article. One is a group of computers on a single physical network segment. The other is an IP network address range that is allocated by a system administrator.
Network address--An IP address with a host portion that is all zeros.
Octet--An 8-bit number, 4 of which comprise a 32-bit IP address. They have a range of 00000000-11111111 that correspond to the decimal values 0-255.
Packet--A unit of data passed over a TCP/IP network or wide area network.
RFC (Request for Comment)--A document used to define standards on the Internet.
Router--A device that passes network traffic between different IP networks.
Subnet Mask--A 32-bit number used to distinguish the network and host portions of an IP address.
Subnet or Subnetwork--A smaller network created by dividing a larger network into equal parts.
TCP/IP--Used broadly, the set of protocols, standards, and utilities commonly used on the Internet and large networks.
Wide area network (WAN)--A large network that is a collection of smaller networks separated by routers. The Internet is an example of a large WAN.
An IP address (short for Internet Protocol address) is a label which is used to identify one or more devices on a computer network, such as the internet. It can be compared to a postal address. An IP address is a long number written in binary. Since such numbers are difficult to communicate, IP addresses are usually written as a set of numbers in a given order. Devices using IP addresses use the internet protocol to communicate.
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority assigns IP addresses to regional internet registries (RIRs). The RIRs assign them to Internet Service Providers. Internet Service Providers then assign IP addresses to their customers. Very often, people have a router or gateway at home, to which they connect computers, printers, and other devices. These routers or gateways are often configured to assign 'local' IP addresses to the devices that are connected.
Each address has two parts: One that specifies the computer or group of computers, and another which specifies the network. A device can have more than one IP address. Certain types of IP addresses are used to address a group of devices, while others are used to address only one device. Certain types of addresses are unique, others can be re-used. A number of IP addresses are used for special purposes, for example to obtain an IP address automatically.
An IP address is converted to physical or Media Access Control Address using the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP). If an IP address is your phone number, then your MAC address is your name. You may change your phone number, but your name will not change.
Example[change | change source]
Suppose one of our friend wants to meet us but they don’t know our address. He asks for our address & then we give our address like 02, Vidyapuri Road, Supaul, Bihar, India. After giving the address, he or she can easily locate our address. The same thing is done in case of internet. Every network is assigned an address.
Who allocates IP Address[change | change source]
IANA (Internet Assigned Numbers Authority) allocates the IP address. IANA is responsible for the IP addressing system
What an IP address looks like[change | change source]
An IP address is a long binary number, made of ones and zeros. An IPv4 address is 32 binary digits (or bits) long. An IPv6 is 128 bits long, allowing many more IP addresses to be used. IP addresses are usually written in human-readable form, where 8 bits are grouped into one octet. IPv4 addresses are usually written as a group of four numbers. Each number can take a value from 0 to 255. IPv6 addresses are written as a group of eight hexadecimal numbers. Many Ipv6 addresses contain many zeroes. There are special rules which say that in certain cases, these zeroes do not need to be written.
Public and private addresses[change | change source]
Certain IP addresses can be assigned freely on the local area network. Since they are not unique, they are not routed on the internet. The addresses which can be freely assigned are called private IP addresses, the ones which are unique are called public. To be routed, a private address needs to be translated into a public one. This process of translating between private and public addresses is called network address translation, or NAT. Routers and firewalls often also perform this task.
Reaching one or more devices[change | change source]
There are three different types of addresses:
- Unicast addresses: The address is assigned to one specific device. This is the most common case, most addresses are unicast addresses.
- Broadcast addresses: address all computers on the same network. There are certain cases where this is useful, for example to obtain a new address automatically. The sender sends the data once, and the devices used for routing the data make copies, as needed.
- Multicast addresses: This case is similar to the broadcast case above: Some devices are interested in receiving certain data, and the network copies the data as needed. The big difference to the broadcast case above is that all devices connected to the broadcast network see the data sent using broadcast. With multicast, devices need to subscribe to see a given content. The devices on the same network that are not subscribed will not see the content.
Unicast: one sender, one receiver
Broadcast: one sender, many receivers, all on the same (sub)network. All devices see the data
Multicast: one sender, many receivers. Only a selected number of devices (usually called subscribers) see the data.
Obtaining a new IP address[change | change source]
There are different ways of getting a new IP address. One of them is called Bootstrap Protocol (usually shortened to BOOTP). The device that needs a new address, does not know what network it is in, so it uses an IP address of all zeroes (0.0.0.0) which it sends as a broadcast to the current network, on a special port. In addition, it sends the MAC address of the network card, plus a 4 byte random number. The BOOTP server will send a reply, also as broadcast, addressed to a different port. The reply will contain the mac address of the client, the random number, and the IP address of the client. When the client receives the data, it will set the address specified. If the BOOTP server is configured that way, it will also send the IP address and hostname of the BOOTP Server, the name and path to a file which should be loaded to boot the client (using TFTP) or the name of a directory, which the client should mount using NFS.
DHCP extends BOOTP, and allows to send more information, such as the address of a time server, or information which is useful for routing.
IP addresses obtained automatically can be dynamic or static. Static addressing means the same machine will always get the same IP address. With dynamic addresses, a device will get the next address which is not used. Dynamic addresses which are used need to be reviewed from time to time. If they are not renewed, they can be used for other devices.
IP Version 4[change | change source]
With IPv4, each address consists of four 8-digit binary numbers, called octets. An IPv4 address is 32 bits in total. The biggest number one can make with 8 regular digits is 99,999,999, but the biggest number one can make with 8 binary digits is 255 (11111111 in binary), so each octet can be any number from 0 to 255.
An IPv4 address could look something like this:
- 198.51.100.137
Each octet is converted to its decimal form and separated by a period.
Also, there are special meanings associated with two different ending numbers. In general, a last number of 0 stands for the network (called base address), and a last number of 255 stands for all hosts on that network (called broadcast address). Computers that are on the same local network share 3 of the 4 numbers. A computer can be on more than one network. It can also have several names.
Public/Private addresses[change | change source]
The problem with IPv4 is that it only allows for 4.3 billion addresses, and we've almost used them all. To delay this, Network Address Translation (NAT) was created. Network Address Translation has a network share one public IP address and give every computer on the network a private IP address. Everyone living in the same house uses the same address, but mail can be meant for multiple different people living in the house.
Special IP addresses[change | change source]
There are some IP addresses that are reserved for special purposes. For example, the address 127.0.0.1 is called the Loopback Address and will 'loop back' any packets sent to this address back to the computer that sent them, like sending mail to yourself. Although this may not seem useful, it is used to test servers.
| 127.0.0.0/8 block | Starting address | Ending address | Number of addresses |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10.0.0.0/8 | 10.0.0.0 | 10.255.255.255 | 16,777,216 |
| 172.16.0.0/12 | 172.16.0.0 | 172.31.255.255 | 1,048,576 |
| 192.168.0.0/16 | 192.168.0.0 | 192.168.255.255 | 65,536 |
Network[change | change source]
It may define as the it identifies the class of network
Host Part[change | change source]
It may be define as the it identifies the host on network
Static IP Address[change | change source]
It is a permanent internet address. It can’t be changed in this we have to configure manually. It is used in smaller network all server uses static IP’s. It is a simple way for Communication.
Dynamic IP Address[change | change source]
(Dynamic means Constantly changing)
It is a temporary internet address. It assigned by a DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server from a specific range of IP address.
Classes Of Ip Address
IPv4 subnetting[change | change source]
To make a network work faster, it is split up into subnets. To do this, an IP address contains a network ID, subnet ID, and a host ID. A special binary number called a Subnet Mask is used to determine the size of the network, subnet, and host IDs.
The original IPv4 only supported 254 networks, so in 1981 the Internet addressing specification was changed to a classful network architecture. Classful network design allowed for a larger number of individual networks. The first three bits of an IP address determined its class. Three classes (A, B, and C) were defined for normal computer communication (Unicast). The size of the network ID was based on the class of the IP address. Each class used more octets for the network ID, making the host ID smaller and reducing the number of possible hosts.
| Historical classful network architecture | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class | First octet in binary | Range of first octet | Network ID | Host ID | Number of networks | Number of addresses |
| A | 0XXXXXXX | 0 - 127 | a | b.c.d | 27 = 128 | 224 = 16,777,216 |
| B | 10XXXXXX | 128 - 191 | a.b | c.d | 214 = 16,384 | 216 = 65,536 |
| C | 110XXXXX | 192 - 223 | a.b.c | d | 221 = 2,097,152 | 28 = 256 |
| D | 1110XXXX | 224 - 254 | a.b.c.d | e | 223 = 2,100,199 | 29 = 512 |
Classful networks have been replaced by Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) since 1993. CIDR also provides a network address and host address. CIDR does not have classes, which means network and host address sizes don't have to be in octets.
An IPv4 Address in CIDR notation looks like
192.168.0.14/24
The slash and number represent the amount of bits that the network id uses, in this case 24 or 3 octets.
IP Version 6[change | change source]
Because IPv4 is only 32 bits, the number of available addresses will run out. To prevent this, an organization called the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) created IP Version 6 (IPv6), which will eventually finish replacing IPv4.
IP Version 6 uses 16 octets, or 128 bits in total. Octets in IPv6 are written in hexadecimal, and separated by colons (:). An IPv6 address might look like this:
- 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334
An IPv6 address can be long and this can lead to mistakes when typing them into the computer or writing them down. There are two ways in which an IPv6 address can be made shorter without leaving anything out:
- Leading zeroes can be left out: 2001:0db8:00b8:0008:0000:0000:0000:0001 becomes 2001:db8:b8:8:0:0:0:1
- Any number of sequential, all-zero 'chunks' may be compressed to simply ::. This can be done only once in the same address: 2001:0db8:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0001 could be written as 2001:db8::1
DNS[change | change source]
DNS stands for Domain Name System
It is also called service server. It is based on client server network architecture. It contain a database of public IP address. DNS is like a phonebook.
Other versions[change | change source]

Which Class Of Ip Address Your System Have Failed
Versions before IPv4 were experimental and never widely used. Version 5 was used exclusively for the Internet Stream Protocol, which was also never widely used.

Ip Address Types Class
